Utility of exFAT partition External hard drive can be used under various OSes such as Windows and Mac OSX. Most HDDs has to format to NTFS or HFS+ so that they can be used under Windows or Mac environments. The name of exFAT gives a hint for its precursors: FAT file system. ExFAT is a newer version of the FAT32 file system, and you can think it this way: it is a middle ground between FAT32 and NTFS file system (New Technology File System). The Pros of exFAT. ExFAT is a file system that is optimized for flash drives.
On the web I have seen several warnings that if one formats an external HD for ExFAT using Disk Utility, it will still not work on Windows*. If you want a HD that truly works on both platforms - Windows and OS X - you need to format it to ExFAT from within Windows.
Has this issue since been resolved and can I now safely format to EXFAT using Disk Utility, or should I still do this on a Windows machine?
Thanks for any help on this.
*Vista and up, ExFAT is per definition not supported for earlier versions of Windows, and earlier versions of OS X for that matter.
Exfat Format Tool
Mac OS X (10.7.5)
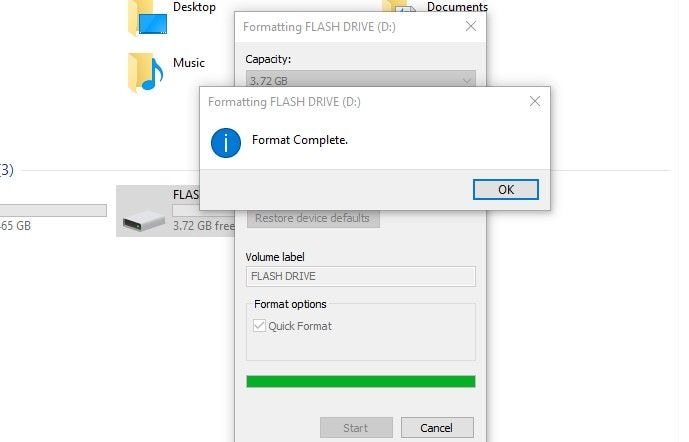
Posted on Dec 5, 2012 12:43 AM
Disk Utility User Guide
Disk Utility on Mac supports several file system formats: Automate mouse movement and clicks.
Apple File System (APFS): The file system used by macOS 10.13 or later.
Mac OS Extended: The file system used by macOS 10.12 or earlier.
MS-DOS (FAT) and ExFAT: File systems that are compatible with Windows.
Apple File System (APFS)
Apple File System (APFS), the default file system for Mac computers using macOS 10.13 or later, features strong encryption, space sharing, snapshots, fast directory sizing, and improved file system fundamentals. While APFS is optimized for the Flash/SSD storage used in recent Mac computers, it can also be used with older systems with traditional hard disk drives (HDD) and external, direct-attached storage. macOS 10.13 or later supports APFS for both bootable and data volumes.
APFS allocates disk space within a container (partition) on demand. When a single APFS container has multiple volumes, the container's free space is shared and is automatically allocated to any of the individual volumes as needed. If desired, you can specify reserve and quota sizes for each volume. Each volume uses only part of the overall container, so the available space is the total size of the container, minus the size of all the volumes in the container.
Choose one of the following APFS formats for Mac computers using macOS 10.13 or later.
APFS: Uses the APFS format. Choose this option if you don't need an encrypted or case-sensitive format.
APFS (Encrypted): Uses the APFS format and encrypts the volume.
APFS (Case-sensitive): Uses the APFS format and is case-sensitive to file and folder names. For example, folders named 'Homework' and 'HOMEWORK' are two different folders.
APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted): Uses the APFS format, is case-sensitive to file and folder names, and encrypts the volume. For example, folders named 'Homework' and 'HOMEWORK' are two different folders.
You can easily add or delete volumes in APFS containers. Each volume within an APFS container can have its own APFS format—APFS, APFS (Encrypted), APFS (Case-sensitive), or APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted).
Format To Exfat On Pc
Mac OS Extended
Choose one of the following Mac OS Extended file system formats for compatibility with Mac computers using macOS 10.12 or earlier.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled): Uses the Mac format (Journaled HFS Plus) to protect the integrity of the hierarchical file system. Choose this option if you don't need an encrypted or case-sensitive format.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled, Encrypted): Uses the Mac format, requires a password, and encrypts the partition.
Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled): Sabrent displaylink driver. Uses the Mac format and is case-sensitive to folder names. Thats them site. For example, folders named 'Homework' and 'HOMEWORK' are two different folders.
Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled, Encrypted): Uses the Mac format, is case-sensitive to folder names, requires a password, and encrypts the partition.
Windows-compatible formats

Posted on Dec 5, 2012 12:43 AM
Disk Utility User Guide
Disk Utility on Mac supports several file system formats: Automate mouse movement and clicks.
Apple File System (APFS): The file system used by macOS 10.13 or later.
Mac OS Extended: The file system used by macOS 10.12 or earlier.
MS-DOS (FAT) and ExFAT: File systems that are compatible with Windows.
Apple File System (APFS)
Apple File System (APFS), the default file system for Mac computers using macOS 10.13 or later, features strong encryption, space sharing, snapshots, fast directory sizing, and improved file system fundamentals. While APFS is optimized for the Flash/SSD storage used in recent Mac computers, it can also be used with older systems with traditional hard disk drives (HDD) and external, direct-attached storage. macOS 10.13 or later supports APFS for both bootable and data volumes.
APFS allocates disk space within a container (partition) on demand. When a single APFS container has multiple volumes, the container's free space is shared and is automatically allocated to any of the individual volumes as needed. If desired, you can specify reserve and quota sizes for each volume. Each volume uses only part of the overall container, so the available space is the total size of the container, minus the size of all the volumes in the container.
Choose one of the following APFS formats for Mac computers using macOS 10.13 or later.
APFS: Uses the APFS format. Choose this option if you don't need an encrypted or case-sensitive format.
APFS (Encrypted): Uses the APFS format and encrypts the volume.
APFS (Case-sensitive): Uses the APFS format and is case-sensitive to file and folder names. For example, folders named 'Homework' and 'HOMEWORK' are two different folders.
APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted): Uses the APFS format, is case-sensitive to file and folder names, and encrypts the volume. For example, folders named 'Homework' and 'HOMEWORK' are two different folders.
You can easily add or delete volumes in APFS containers. Each volume within an APFS container can have its own APFS format—APFS, APFS (Encrypted), APFS (Case-sensitive), or APFS (Case-sensitive, Encrypted).
Format To Exfat On Pc
Mac OS Extended
Choose one of the following Mac OS Extended file system formats for compatibility with Mac computers using macOS 10.12 or earlier.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled): Uses the Mac format (Journaled HFS Plus) to protect the integrity of the hierarchical file system. Choose this option if you don't need an encrypted or case-sensitive format.
Mac OS Extended (Journaled, Encrypted): Uses the Mac format, requires a password, and encrypts the partition.
Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled): Sabrent displaylink driver. Uses the Mac format and is case-sensitive to folder names. Thats them site. For example, folders named 'Homework' and 'HOMEWORK' are two different folders.
Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled, Encrypted): Uses the Mac format, is case-sensitive to folder names, requires a password, and encrypts the partition.
Windows-compatible formats
Choose one of the following Windows-compatible file system formats if you are formatting a disk to use with Windows.
MS-DOS (FAT): Use for Windows volumes that are 32 GB or less.
ExFAT: Use for Windows volumes that are over 32 GB.
